dehydrated carrot powder price
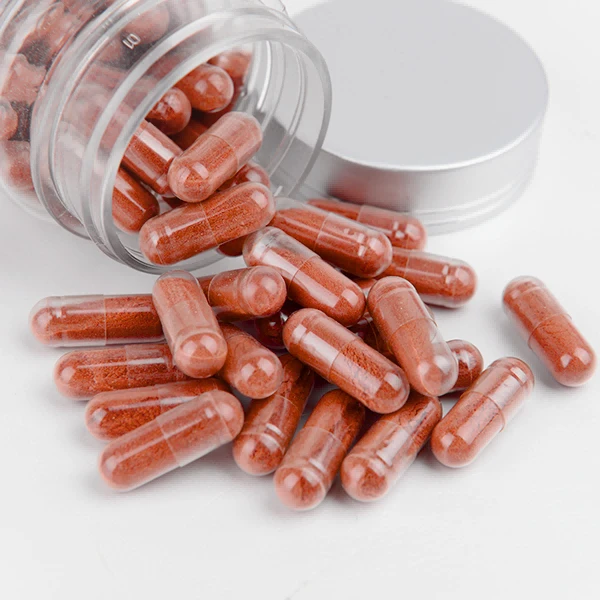
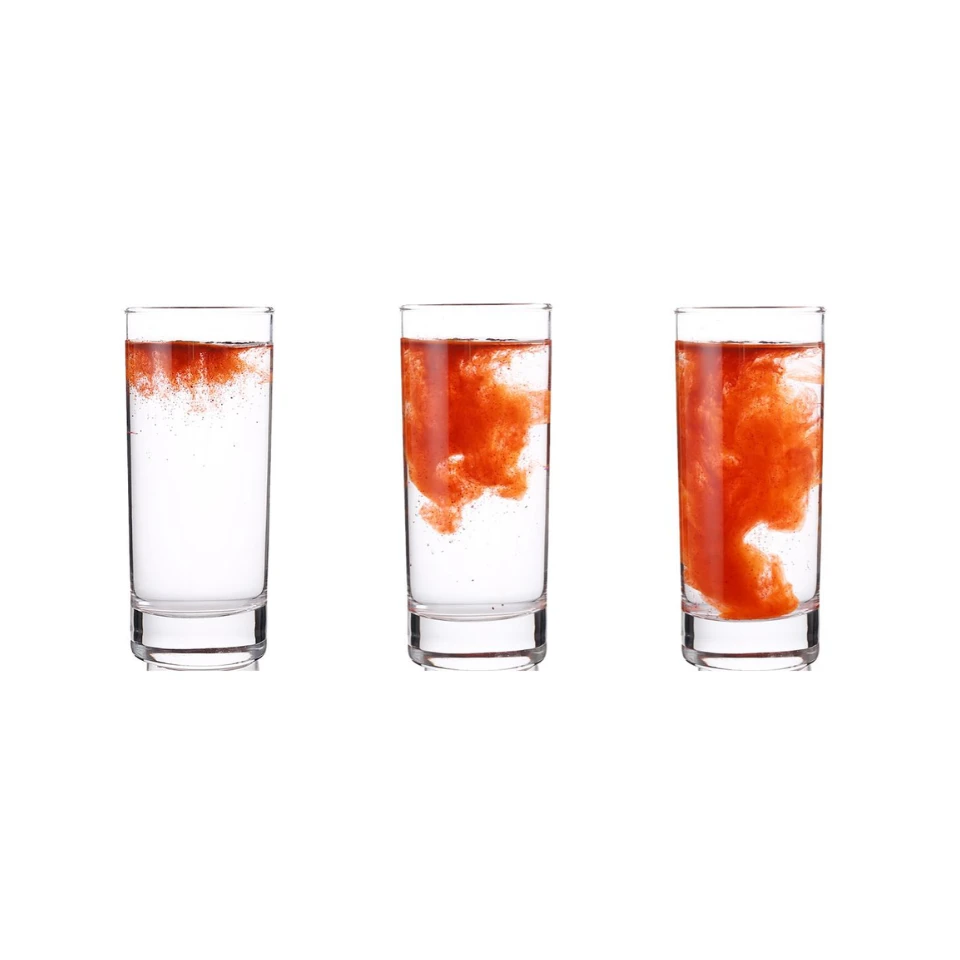
Inulin Powder from Chicory: the quiet workhorse of sugar reduction If you work in R&D or sourcing, you’ve probably noticed how quietly chicory inulin has gone mainstream. Our pick— Inulin Powder Chicory Root Extract Natural Sweentener Sugar Substitutes —comes out of a facility in the Zhengding Area of China (Hebei) Pilot Free Trade Zone. It’s a prebiotic fiber first, a sugar substitute second, and a texture magician somewhere in between. Many customers say it’s the easiest way to trim sucrose without wrecking mouthfeel. Why inulin is trending (and fast) Two forces push this along: global sugar-reduction targets and the recognition of inulin as a dietary fiber by major regulators. Actually, the data is clear—brand teams want ≤10 g sugar per serving without losing body, and inulin delivers bulking, mild sweetness, and prebiotic benefits. Surprisingly robust in bakery and dairy, too. Product snapshot Item Spec (typical) Method / Standard Appearance White to off‑white powder Visual Inulin (dry basis) ≥ 90% HPLC (fructan) Degree of Polymerization DP ≈10–60 (blend) HPAEC‑PAD Moisture ≤ 5.0% Loss on drying Ash ≤ 0.2% Gravimetric Mesh size 60–200 mesh (custom) Sieve analysis TPC / Yeast & Mold ≤1.0×10³ / ≤100 CFU/g ISO 4833-1 / 21527-1 Heavy metals Pb, As, Cd, Hg ≤ limits ICP‑MS Shelf life 24 months, cool & dry Real‑world use may vary Source: Cichorium intybus L.; Non‑GMO, BSE/TSE‑free, non‑irradiation, allergen‑free. How it’s made (short version) Materials: selected chicory roots; potable water. Methods: hot water extraction → filtration → ion‑exchange demineralization → vacuum evaporation → spray‑drying → milling & sieving. Controls: metal detection, nitrogen flushing, tamper‑evident packaging. Testing standards: AOAC 2011.25 (dietary fiber), HPLC for fructans, ISO microbiology, ICP‑MS for metals. Stability: pH 4–7; heat tolerant to ≈160°C for short bakes. Where it works best Beverages (5–7% for body), yogurts and ice cream (2–6% for creaminess), breads/cookies (3–10% for sugar cut + fiber), nutrition bars, meal shakes, and even gummy supplements. I guess the most underrated use is pairing with stevia/monk fruit to mask aftertaste. Pharma teams use it as a filler/binder, too. Advantages: prebiotic support, mild sweetness (~0.1–0.2× sucrose), low glycemic, fat mimicry, and label‑friendly fiber claims (verify per market). Vendor snapshot (quick compare) Vendor Certs Assay Customization Lead time Finutra (Zhengding, Hebei) ISO 22000, HACCP, Halal, Kosher ≥90% Mesh 60–200; agglomerated; custom DP ≈7–12 days EU Chicory Supplier A BRC, FSSC 22000 ≥90% Agglomerated only ≈2–3 weeks Agglomerated Brand B IFS, Kosher ≥85–90% Limited mesh options around 3 weeks Customization, packaging, and paperwork Inulin Powder Chicory Root Extract Natural Sweentener Sugar Substitutes ships in 25 kg PE-lined paper bags or 1 kg pouches for pilots, lot-traceable from Building 23B1, No.2 Yuanboyuan St., Zhengding Area. Custom options: agglomerated instant grade for beverages, DP‑tuned blends, and flavor‑ready carriers. COA, MSDS, Non‑GMO and allergen statements supplied; Halal/Kosher available. Mini case: low‑sugar yogurt A dairy client swapped 4% sucrose with 3% Inulin Powder Chicory Root Extract Natural Sweentener Sugar Substitutes plus stevia (200 ppm). Sensory panel (n=30) reported better creaminess and 18% higher “natural sweetness” scores; syneresis dropped ≈12% after 14 days at 4°C. To be honest, the texture gain was the clincher. Compliance notes Recognized as dietary fiber by the FDA; check local labeling rules. Claims around digestive benefits vary by market; substantiate per EFSA or local guidance. Run pilot validation: pH impact, freeze/thaw, and water activity. Real-world use may vary. If you need a bench sample of Inulin Powder Chicory Root Extract Natural Sweentener Sugar Substitutes , ask for DP profile and mesh spec up front; it saves a week of reformulation back‑and‑forth. Authoritative citations FDA. Guidance for Industry: Declaration of Certain Isolated or Synthetic Non‑Digestible Carbohydrates as Dietary Fiber (2018). https://www.fda.gov EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies. Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for carbohydrates and dietary fibre. EFSA Journal (2010). https://www.efsa.europa.eu AOAC Official Method 2011.25. Total Dietary Fiber in Foods. https://www.aoac.org ISO 22000:2018 Food safety management systems — Requirements. https://www.iso.org
Finutra devotes to be an integrated supplier for global supply chain, we offer a
broad array of raw materials and functional ingredients
Authoritative Certification
Continuous Innovation, Customer First
Enhance core competitiveness to bring customers better products and services,
Each of these is the result of our team's relentless pursuit of excellence
and our deep commitment to social responsibility.








Global
Reach
FINUTRA has over 350,000 square feet of manufacturing and warehouse
space worldwide.
Industries We Serve
Advanced molecular distillation and microencapsulation
technology. Extremely bioavailable
trace carotenoids Intuitively soluble.


STAY UPDATED
Receive special offers and first look at new
products.
products.
Building 23B1, No.2 Yuanboyuan St., Zhengding Area of China (Hebei) Pilot Free Trade Zone
QUICK LINK
Finutra devotes to be an integrated supplier for global supply chain, we offer a broad array of raw
materials and functional ingredients as a manufacturer, distributor and supplier for global Beverage,
Nutraceutical, Food, Feed and Cosmeceutical.
Copyright © 2025 Hebei Finutra
Biotech Co.,
Ltd. All
Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy